MSPowerBI: Difference between revisions
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
* select dots [[File:PowerBI_0.JPG|400px]] | * select dots [[File:PowerBI_0.JPG|400px]] | ||
* select export data [[File:PowerBI_1.JPG|400px]] | * select export data [[File:PowerBI_1.JPG|400px]] | ||
===Relationsships=== | |||
====Change Default Summarization==== | |||
* [[File:PowerBI_18.PNG|600px]] | |||
Revision as of 22:06, 2 March 2022
Information
- extension for local saves is *.pbix
Concepts
- There are three different options on how your data should be treated: Import, DirectQuery, or Live Connection. This section will focus specifically on the Import option.
Power Query
Eine Power Query benutzerdefinierte Funktion ist eine Zuordnung aus einem Satz von Eingabewerten zu einem einzelnen Ausgabewert und wird aus nativen M-Funktionen und -Operatoren erstellt.
M Language
M ist eine funktionale Sprache:
- Der gesamte Code ist in Schritte unterteilt, die alle innerhalb eines Let-in-Statements definiert sind
- Jeder Schritt hat einen Namen, z. B. Quelle, oder auch #"Geänderter Typ"
- Schritte bauen zumeist (aber nicht zwangsläufig) aufeinander auf. Daher sieht man es häufig, dass der Name eines Schrittes im darauffolgenden Schritt innerhalb der Funktionen benutzt wird
- Derjenige Schritt, der nach dem in benannt ist (letzte Zeile im Skript), stellt das Ergebnis der gesamten Abfrage da. Das Ergebnis dieses Schrittes wird dem Nutzer – zumeist, aber nicht notwendigerweise – als Tabelle zurückgegeben.
Relationsships
Import aspects are:
- Auto-detected relationships
- There may be only one active relationship between two tables
- There may be an unlimited number of in-active relationships between two tables
- Relationships may only be built on a single column, not multiple columns
- Relationships automatically filter from the one side of the relationship to the many side Relationships cannot be built directly between tables that have a many-to-many relationship
- Cross-Filtering means a filter from a 1-to-many and many-to-1 relationship like filter on one dimension table to filter another dimension table via a fact table
The arrows defines the direction of filtering:
Views
Ressources
Operation
Import Data from Excel
General Information
Power Query Editor always works with a preview of the data, to make the development process fast. When you load the data in Power BI, transformations will be applied on the entire dataset. Hence errors might have not been identified before the full import of data.
Steps
Define Import
- select import and file
- select transform (not load)
Delete Rows e.g. Header
Delete Columns
- delete columns not needed by right click -> delete
Add Columns
- see https://docs.microsoft.com/de-de/power-bi/transform-model/desktop-tutorial-create-calculated-columns
- example
= Table.AddColumn(#"Geänderter Typ", "Charge Fact", each if Value.Is([#"Chargeability (FTE)#(lf)"], type number) then [#"Chargeability (FTE)#(lf)"] else 1)
= Table.AddColumn(#"Geänderter Typ2", "Activity Type", each if [#"Partner-PSP-Element"] = "9914.P10048.004" then "ES Admin" else if [#"Partner-PSP-Element"] = "9914.P10048.005" then "ES Training" else if [#"Partner-PSP-Element"] = "9914.P10048.006" then "ES Relationship Management" else "tbd")
Delete Rows
- filter specific value (click to right down arrow in the column header and define the filter)
N charactors from left
Adjust Query
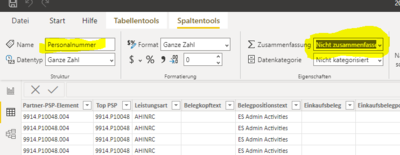
Not summing up a column like personnel number
Error Handling
Export Data to Excel
Relationsships
Change Default Summarization
Visuals
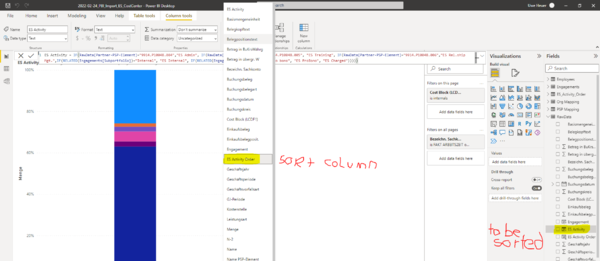
Sorting according to Values
ES Activity Order = RELATED(ES_Activity_Order[ES Activity Order])
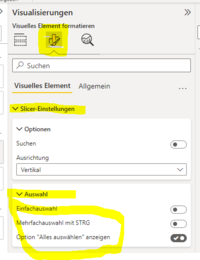
Slicer
Matrix
- is neary the same as pivot
- https://www.goodly.co.in/create-pivot-table-in-power-bi/
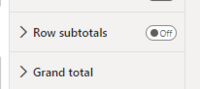
- grand total and subtotals
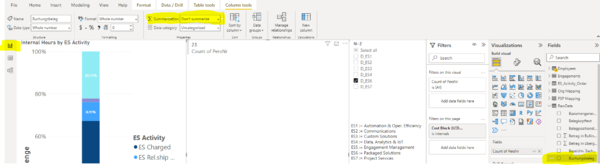
Stacked Bar Chart
- figures in bar by switching on 'data label'
English/German
| Slicer | Datenschnitt |
| E1 | G1 |
| E2 | G2 |