MSPowerBI
Information
- extension for local saves is *.pbix
Concepts
- What is Power BI
- https://docs.microsoft.com/de-de/power-bi/guidance/star-schema
- There are three different options on how your data should be treated: Import, DirectQuery, or Live Connection. This section will focus specifically on the Import option.
Power Query
Eine Power Query benutzerdefinierte Funktion ist eine Zuordnung aus einem Satz von Eingabewerten zu einem einzelnen Ausgabewert und wird aus nativen M-Funktionen und -Operatoren erstellt.
M Language
M ist eine funktionale Sprache:
- Der gesamte Code ist in Schritte unterteilt, die alle innerhalb eines Let-in-Statements definiert sind
- Jeder Schritt hat einen Namen, z. B. Quelle, oder auch #"Geänderter Typ"
- Schritte bauen zumeist (aber nicht zwangsläufig) aufeinander auf. Daher sieht man es häufig, dass der Name eines Schrittes im darauffolgenden Schritt innerhalb der Funktionen benutzt wird
- Derjenige Schritt, der nach dem in benannt ist (letzte Zeile im Skript), stellt das Ergebnis der gesamten Abfrage da. Das Ergebnis dieses Schrittes wird dem Nutzer – zumeist, aber nicht notwendigerweise – als Tabelle zurückgegeben.
Relationsships
Import aspects are:
- Auto-detected relationships
- There may be only one active relationship between two tables
- There may be an unlimited number of in-active relationships between two tables
- Relationships may only be built on a single column, not multiple columns
- Relationships automatically filter from the one side of the relationship to the many side Relationships cannot be built directly between tables that have a many-to-many relationship
- Cross-Filtering means a filter from a 1-to-many and many-to-1 relationship like filter on one dimension table to filter another dimension table via a fact table
The arrows defines the direction of filtering:
Hierachies
Modelling Organizational Hierachies
- https://ssbi-blog.de/blog/business-topics/wie-du-unregelmaessige-hierarchien-in-power-bi-und-power-pivot-nutzen-solltest/ fixed number of levels
- https://www.daxpatterns.com/parent-child-hierarchies/
- https://radacad.com/parsing-organizational-hierarchy-or-chart-of-accounts-in-power-bi-with-parent-child-functions-in-dax with two columns representing a parent relationship
- https://radacad.com/removing-blanks-from-organizational-ragged-hierarchy-in-power-bi-matrix-visual
- https://radacad.com/dynamic-row-level-security-with-organizational-hierarchy-power-bi
Calculated Columns
ES Activity Order = RELATED('ES Activity Order'[ES Activity Order])
Measures
Calculated measures are very different than calculated columns. Calculated measures are not static, and operate within the current filter context of a report; therefore, calculated measures are dynamic and ever-changing as the filter context changes. Calculated measures can do the following:
- They can be assigned to any table
- They interact with all the relationships in the data model automatically, unlike calculated columns.
- They are not materialized in a column, and therefore cannot be validated in the Data View.
Filter Context
Der Filterkontext beschreibt die Filter, die während der Auswertung eines Measures oder eines Measureausdrucks angewandt werden. Filter können direkt auf Spalten angewandt werden. Darüber hinaus können Filter auch indirekt angewandt werden. Dies passiert immer dann, wenn Filter durch Modellbeziehungen an andere Tabellen weitergegeben werden.
Change of the Filter Context
Es gibt zwei mögliche Standardergebnisse, wenn Sie der CALCULATE-Funktion Filterausdrücke hinzufügen:
- Wenn sich die Spalten (oder Tabellen) nicht im Filterkontext befinden, werden dem Filterkontext neue Filter hinzugefügt, um den CALCULATE-Ausdruck auszuwerten.
- Wenn sich die Spalten (oder Tabellen) bereits im Filterkontext befinden, werden die vorhandenen Filter durch neue Filter überschrieben, um den CALCULATE-Ausdruck auszuwerten.
CALCULATE(<EXPRESSION>, [<FILTER>*])
ALL
- removes all filter
- https://radacad.com/how-to-use-all-in-a-dax-expression-in-power-bi Many examples to ignore filter by specific slicers or other visuals or in total
FILTER
The following definitions are equivalent
Revenue Red = CALCULATE([Revenue], 'Product'[Color] = "Red")
Revenue Red = CALCULATE([Revenue],
FILTER(
'Product',
'Product'[Color] = "Red"
)
)
REMOVEFILTERS
Examples
- https://www.enjoysharepoint.com/power-bi-measure-examples/ examples
- avoid blank values
Menge UH = IF( ISBLANK(SUM(CostCenterRawData[Menge])), 0, SUM(CostCenterRawData[Menge]))
Full Productive Capacity = CALCULATE(
COUNT(Employees[Chargeability]), ALL(CostCenterRawData), Employees[Practice] IN ALLSELECTED(CostCenterRawData[N-2]), Employees[Legal_company] = "EDT", Employees[Chargeability] = 1.0)
Partly Productive Capacity = CALCULATE(
COUNT(Employees[Chargeability]), ALL(CostCenterRawData), Employees[Practice] IN ALLSELECTED(CostCenterRawData[N-2]), Employees[Legal_company] = "EDT", Employees[Chargeability] < 1.0, Employees[Chargeability] > 0.0)
All Utilization Hours = CALCULATE('CostCenterRawData'[Utilization Hours], REMOVEFILTERS(CostCenterRawData[ES Activity]))
DAX
DAX Studio
Views
Ressources
- Microsoft Documentation
- Beginners Tutorial
- examples for data manipulation at import
- irregular hierachies e.g. for org model
Operation
Import Data from Excel
General Information
Power Query Editor always works with a preview of the data, to make the development process fast. When you load the data in Power BI, transformations will be applied on the entire dataset. Hence errors might have not been identified before the full import of data.
Steps
Define Import
- select import and file
- select transform (not load)
Delete Rows e.g. Header
Delete Columns
- delete columns not needed by right click -> delete
Add Columns
- see https://docs.microsoft.com/de-de/power-bi/transform-model/desktop-tutorial-create-calculated-columns
- example
= Table.AddColumn(#"Geänderter Typ", "Charge Fact", each if Value.Is([#"Chargeability (FTE)#(lf)"], type number) then [#"Chargeability (FTE)#(lf)"] else 1)
= Table.AddColumn(#"Geänderter Typ2", "Activity Type", each if [#"Partner-PSP-Element"] = "9914.P10048.004" then "ES Admin" else if [#"Partner-PSP-Element"] = "9914.P10048.005" then "ES Training" else if [#"Partner-PSP-Element"] = "9914.P10048.006" then "ES Relationship Management" else "tbd")
Delete Rows
- filter specific value (click to right down arrow in the column header and define the filter)
N charactors from left
Adjust Query
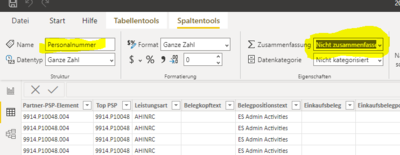
Not summing up a column like personnel number
Error Handling
Export Data to Excel
Relationsships
Change Default Summarization
Visuals
General Properties
Filter on Visuals
Show Selection Pane for Grouping
- you need to select at least 2 visuals to have the context menu 'group'
- to avoid overlapping visuals put them in different groups
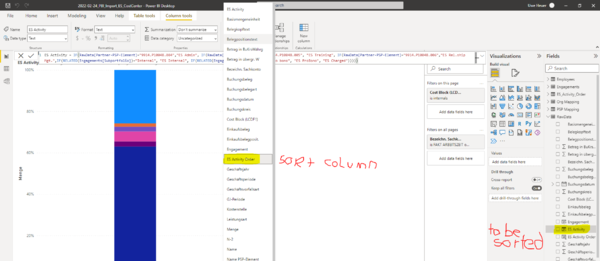
Sorting according to Values
ES Activity Order = RELATED(ES_Activity_Order[ES Activity Order])
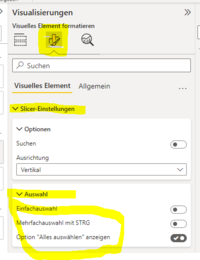
Slicer
Matrix
- is neary the same as pivot
- https://www.goodly.co.in/create-pivot-table-in-power-bi/
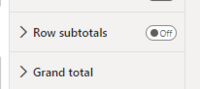
- grand total and subtotals
Mulit-Row Card
- Title On/Off: caption of multi-row card on top
- Visual Data -> Fields -> Right Click -> Rename for this visual: text below number
- Visual Data -> Category Label On/Off: show text below number
- Visual Data -> Category Label: format of text below number
Pie Chart
- sequence of fields defines the position, starts at 00:00
- Format -> Visual -> Legend -> Position
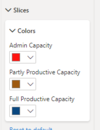
- Format -> Visual -> Slices -> Colors
Single Card
- 'Collout value' -> Font: size of number
- 'Category label' on/off: text below number
- 'Title': text above number
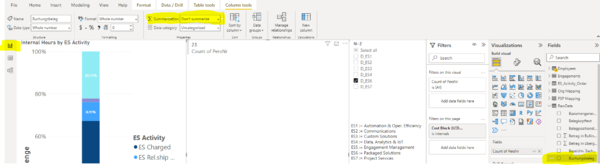
Stacked Bar Chart
100% Stacked Column Chart
Stacked Column Chart
- show 0 values
Table
Show Duplicates
Projects
ES KPI Reporting
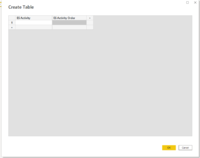
- Table for Activity Sorting: Report View -> Enter Data -> ... and edit it via these steps
English/German
| Slicer | Datenschnitt |
| E1 | G1 |
| E2 | G2 |