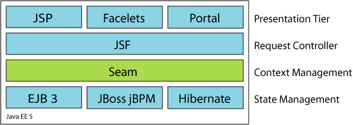
Seam
Introduction
Seam manages components, that means it manages the complete lifecycle and scope of the components (inversion of control principle), named as context of a component. Thereto it injects dependencies to the components (dependency injection).
Most Seam application use session beans as JSF action listeners.
Seam lets you use a JSF EL expression inside EJB-QL. Under the covers, this results in an ordinary JPA setParameter() call on the standard JPA Query object.
Seam integrates Hibernate Validator and lets you use it for data validation (even if you are not using Hibernate for persistence).
Installation and Configuration
- download jboss-seam-2.0.2.SP1.zip and extract to <ECLIPSE_WORKSPACE>
- add jboss.home to <SEAM_DIR>\build.properties
Libs
| jboss-seam.jar | Provides the Seam container, Seam annotations, bijection, extended JSF life cycle, CRUD framework, security, jBPM integration, Drools integration, web services, page flows, asynchronous support, conversations, extended EL, managed transactions and persistence, and the integration test framework. |
| jboss-seam-remoting.jar | Supports invoking Seam components using Ajax requests and allows JavaScript to listen for messages on JMS queues and topics |
| jboss-seam-ui.jar | Includes the Seam JSF components, file upload capability, graphics generation, Facelet integration, and conversation controls |
| jboss-seam-debug.jar | Activates the hot deployment classloader and provides a Seam debug page and developer-oriented error page |
| jboss-seam-ioc.jar | Provides integration with Spring and other IoC containers |
| jboss-seam-pdf.jar | Has support for generating PDF files using Facelet templates and a document storage mechanism for pushing binary files |
| jboss-seam-mail.jar | Provides email integration and supports creating emails from Facelet templates |
Annotations
Seam defines own annotations and uses some other annotations.
org.hibernate.validator.Length
@org.hibernate.validator.Length(min=<Number>, max=<Number>) <attribute declaration>
for length validation.
org.hibernate.validator.NotNull
@org.hibernate.validator.NotNull <attribute declaration>
for validation.
org.jboss.seam.annotations.datamodel.DataModel
@org.jboss.seam.annotations.datamodel.DataModel <attribute declaration>
The @DataModel annotation exposes an attibute of type java.util.List to the JSF page as an instance of javax.faces.model.DataModel. This allows us to use the list in a JSF <h:dataTable> with clickable links for each row. In this case, the DataModel is made available in a session context variable named messageList.
org.jboss.seam.annotations.datamodel.DataModelSelection
@org.jboss.seam.annotations.datamodel.DataModelSelection <attribute declaration>
The @DataModelSelection annotation tells Seam to inject the List element that corresponded to the clicked link.
org.jboss.seam.annotations.In
@org.jboss.seam.annotations.In <attribute_declaration>
The attribute is injected by Seam. Examples for injections are EntityManager or FacesMessages.
org.jboss.seam.annotations.Logger
@org.jboss.seam.annotations.Logger
The annotation is used to inject the component's Log instance. The logger has a specialised syntax e.g.
log.info("creating component '#0' on #1", name(), date());
log.info("#{<object>.<attribute>}");
org.jboss.seam.annotations.Name
@org.jboss.seam.annotations.Name("<Name>")
<class_declaration>
specifies the name of the Seam component. This name must be unique within the Seam application. When JSF asks Seam to resolve a context variable with a name that is the same as a Seam component name, and the context variable is currently undefined (null), Seam will instantiate that component, and bind the new instance to the context variable.
org.jboss.seam.annotations.Scope
@org.jboss.seam.annotations.Scope(org.jboss.seam.ScopeType.<SCOPE_TYPE>) <class_declaration>
specifies the scope of a seam component. Each Seam component has a default scope. Types are:
| Type | Description | Default for |
| EVENT | the component lives only for one method call | JavaBeans |
Standard components
Identiy
@In Identity idendity;
is a standard component of the Seam security model und lives as long as the session.
API
FacesMessages
FacesMessages.instance().add("...");
Seam tags
Seam use Facelets for the user interface. An example of an xhtml file is
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:s="http://jboss.com/products/seam/taglib" xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core">
validateAll
This JSF component tells JSF to validate all contained input fields against the Hibernate Validator annotations specified in the entitiy bean.
Applications
- s. JBoss
Reources
- Seam in Action by Dan Allen in C:\Uwes\Documents\Software_Development\Programming\Frameworks\Seam\SeaminAction.pdf, Source code extracted to <ECLIPSE_WORKSPACE>/seaminaction