Git
Concepts
Git is a Distributed Version Control Systems (DVCS). Clients don’t just check out the latest snapshot of the files: they fully mirror the repository. Thus if any server dies, and these systems were collaborating via it, any of the client repositories can be copied back up to the server to restore it. Every clone is really a full backup of all the data. In a DVCS the elemental concept is a change set, it is merely a change to a set of files and a pointer to the previous change set. For identification the change set includes a pointer to the previous change set and which is hashed then. A changeset is merely a change to a set of files. Git changesets are identified by an SHA-1 hash. The tip of the current branch is referred to as HEAD.
For Git a version history is a stream of snapshots of the complete project. Therefore the local repository contains the complete history of a project. Conceptually a commit object (short:commit) represents a version of all files tracked in the repository at the time the commit was created. A remote repository on a server typically does not require a working tree. A Git repository without a working tree is called a bare repository.
Git has three main states that your files can reside in: committed, modified, and staged.
- Committed (Tracked) means that the data is safely stored in your local database (git commit).
- Modified means that you have changed the file but have not committed it to your database yet.
- Staged means that you have marked a modified file in its current version to go into your next commit snapshot (git add).
- Untracked means the file is not tracked by the Git repository. This means that the file never staged nor committed.
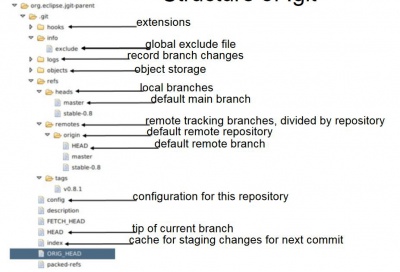
Repository
A Repository is essentially a folder on the local hard disk which contains the working directory and the metadata folder (git directory). The Git directory (.git) is where Git stores the metadata and object database for your project. This is the most important part of Git, and it is what is copied when cloning a repository from another computer.
Working Directory
The working directory is the directory used to modify files for the next commit (it seems that it is sometimes also called working tree). By default it is located one level above the .git directory. It is a single checkout of one version of the project. These files are pulled out of the compressed database in the Git directory and placed on disk for you to use or modify. It corresponds to a checkout of one version of the repository with potential changes done by the user. The user can change the files in the working tree by modifying existing files and by creating and removing files.
\<Repository>\ // Working Directory \.git\ // Git Directory
Staging Area
The staging area or index is a file (.git/index) filled by git add, generally contained in your Git directory, that stores information about what will go into your next commit.
Cloning is the process of copying an existing Git repository via the Git tooling. Pushing means sending a new version in the local repository to a remote repositories.
A URL in Git determines the location of the repository.
A tag points to a commit which uniquely identifies a version of the Git repository. The benefit of tags is to mark the repository for a specific reason, e.g., with a release.
Git can be configured to ignore certain files and directories for repository operations. This is configured via one or several .gitignore files. Typically, this file is located at the root of your Git repository but it can also be located in sub-directories. In the second case the defined rules are only valid for the sub-directory and below.
Configuration
See installation information for the different computers (e.g. Eon Laptop New):
- HOME directory: git, EGit, ... need this path for looking up the global user configuration (.gitconfig). HOME should point to your home directory. Git installation routine put .gitconfig to C:\Users\U1728. If %HOME% is not set %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH% is used.
Operations
Add File to be tracked
git add <Filename>
Delete a Repository
Delete the folder which contains the repository.
Egit
The decoration is shown in the views 'package explorer', 'project explorer' and 'navigator'. The decorations icons are:
Gitting an Eclipse Project
There is a discussion if you should put multiple projects in one git repository or having a git repository for each eclipse projects. It seems that the second options is better if the projects are not related. The same applies to what should be included in a git repository and what should be ignored.
See list below which files and folders should be in scope of git:
- \src\...
- \.settings\
- \.classpath
- \.project
See list below which should be ignored:
- \bin\... // or anything which can be recreated