TypeScript
Concept[edit]
TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript. TypeScript wird während des Entwicklungsvorgangs mit Hilfe eines Transpilers (eine Sonderform eines Compilers) in JavaScript übersetzt. The concepts and features below are add-ons to the JavaScript language. The main benefits are:
- TypeScript provides the static type system which provides great help in catching programming errors at compile time.
- Typescript brings Types, Classes, interfaces & modules. it makes the code more maintainable and scalable.
- Typescript comes with several language features. It supports Encapsulation through classes and modules. Supports constructors, properties & functions. It has support for Interfaces. You can make use of Arrow functions or lambdas or anonymous functions.
Language[edit]
Statements[edit]
Statements end with a ; but if it is a single line statement it might be ommitted.
Data Types[edit]
JavaScript has eight data types. The primitive types are
- number
- string
- boolean
- bigint
- symbol
- undefined, and
- null.
Everything else is an object. The TypeScript Type System supports all of them and also brings its own special types. They are unknown, any, void & never.
Type Annotations[edit]
funcXYZ : <RETURN_TYPE> {
}
varXYZ : <TYPE> = ...;
Union types[edit]
The union types are special. They allow a variable to be of either of two types:
var x: string | number;
Variable Declaration[edit]
- let variables are available in block, var variables are available in the function
- see also here
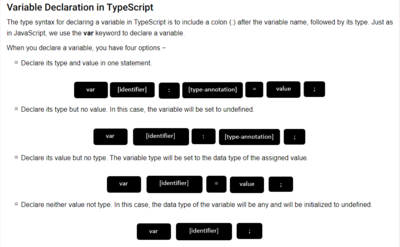
- <code? after the variable name is short of
<TYPE>|undefined
Classes[edit]
- TypeScript offers special syntax for turning a constructor parameter into a class property with the same name and value. If access modifiers there is no need to declare properties
export class Menu {
constructor(
public id: number,
public parent_id: number,
public name: string,
public comment: string
) {
Interfaces[edit]
Typescript uses in interface in multiple ways (s. here):
- no access modifiers, everything is public
interface <INTERFACE_NAME> {
...
implements <INTERFACE_NAME>
...
Access Modifier[edit]
- private
- protected
- public
Generics[edit]
Functions[edit]
Function Parameters[edit]
function doSomething(value: any, options?: <TYPE>) // options parameter is optional
Decorators[edit]
A Decorator is a special kind of declaration that can be attached to a class declaration, method, accessor, property, or parameter. Decorators use the form @<Expression>, where <Expression> must evaluate to a function that will be called at runtime with information about the decorated declaration.
Non-null assertion/Bang operator[edit]
When you add an exclamation mark after variable/property name, you're telling to TypeScript that you're certain that value is not null or undefined, which prevents the ts2564 compilation error.
Optional Chaining Operator[edit]
The ?. operator always produces the value undefined when it stops descending into a property chain, even when it encounters the value null.
Import/Export[edit]
Starting with ECMAScript 2015, JavaScript has a concept of modules. TypeScript shares this concept. Each ts-file is javascript module.
import { ZipCodeValidator } from "./ZipCodeValidator"; // import a single export from a module
Installation[edit]
C:\Uwes\Programme\nodejs>npm install -g typescript
