Angular
Concept[edit]
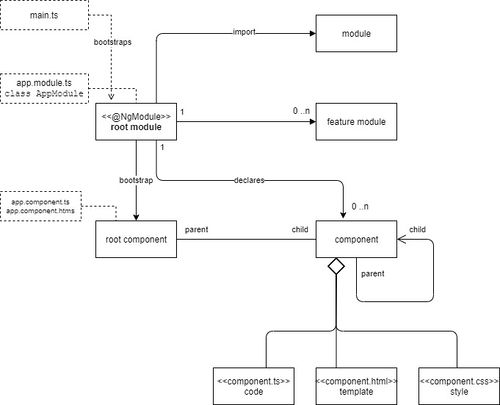
Angular is a platform and framework for building single-page client applications using HTML and TypeScript. Angular is written in TypeScript. It implements core and optional functionality as a set of TypeScript libraries that you import into your apps.
[file:///C:/Uwes/owncloud/documents/Software_Development/Programming/Frameworks/Angular/Angular.drawio]
Modules[edit]
The basic building blocks are NgModules, which provide a compilation context for components and which bundles different Angular building blocks. An Angular app is defined by a set of NgModules. An app always has at least a root module conventionally named AppModule that enables bootstrapping, and typically has many more feature modules. Like JavaScript modules, NgModules can import functionality from other NgModules, and allow their own functionality to be exported and used by other NgModules. For example, to use the router service in your app, you import the Router NgModule.
@NgModule
Components[edit]
Every Angular application has at least one component, the root (top level) component that connects a component hierarchy (component tree) with the page document object model (DOM). A component controls a patch of screen called a view. Each component defines a selector, a class that contains application data and logic (view logic), and is associated with an HTML template that defines a view to be displayed in a target environment (see @Component).
Root Component[edit]
- see
<APP_ROOT_DIR>\src\app.component.* - change title in
app.component.ts
Own Components[edit]
A component instance has a lifecycle that starts when Angular instantiates the component class and renders the component view along with its child views. The lifecycle continues with change detection, as Angular checks to see when data-bound properties change, and updates both the view and the component instance as needed. The lifecycle ends when Angular destroys the component instance and removes its rendered template from the DOM.
@Component({ // from angular core
selector: '<SELECTOR>', // tag name within html
templateUrl: '<PATH_FILENAME>', // path and filename of the corresponding template
template: '<HTML_CODE>', // e.g. <h1>{{title}}</h1>
styleUrls: // the styles only apply to the component
})
export class <COMPONENT_CLASS> [implements OnInit] {
[ngOnInit() { // is called shortly after creating a component
}]
}
In addition each component needs to be declared in a module, normally in @NgModule ... AppModule
Components use services.
Parent/Child Component Relation[edit]
A parent child relation is established by using the selector of the child component in the template of the parent component.
Templates[edit]
The metadata for a component class associates it with a template that defines a view. A template combines ordinary HTML with Angular directives and binding markup that allow Angular to modify the HTML before rendering it for display. The metadata for a service class provides the information Angular needs to make it available to components through dependency injection (DI).
{{<PROPERTY>}} // data binding to property of component class
{{<OBJECT>.<PROPERTY>}}
{{todo.targetDate}} | date // pipes are date, lowercase, uppercase, ...
(<EVENT>)=<METHOD> // event binding
[(ngModel)]="<PROPERTY_NAME>" // two-way data and event binding, for piping it has to be split into [ngModel]="... | <PIPE>" and (ngModel)
<a routerLink="/todos">here</a> // router link
Directives
Two-way binding notation '[()]' is also called banana-in-the-box.
Template Variables[edit]
Template Variables are defined by the prefix #<NAME>. They can be referenced e.g. in the template in Typescript code e.g.
... <button type="button" (click)="callPhone(<NAME>.value)">Call</button> ...
Template Input Variables[edit]
The let keyword declares a template input variable that you can reference within the template e.g.
// see bookmarks.component.html <ng-template matMenuContent let-subMenuIndex="subMenuIndex"> <button mat-menu-item (click)="onViewMenu(subMenuIndex)">View Menu</button>
ng-template[edit]
With <ng-template> you can define template content that is only being rendered by Angular when you, whether directly or indirectly.
Standard Events[edit]
- click
- dblclick
- focus
- blur
- submit
- scroll
- cut
- copy
- paste
- keydown
- keypress
- keyup
- mouseenter
- mousedown
- mouseup
- drag
- dragover
- drop
Custom Events[edit]
- sending custom events from child to parent
@Component ...
export class ... {
@Output() public <EVENT_NAME> = new EventEmitter[<<EVENT_TYPE>>](); // from @angular/core
...
<METHOD>() {
this.<EVENT_NAME>.emit([<VARIABLE_OF_EVENT_TYPE>]);
- catching event in parent in parent HTML file:
<<COMPONENT_SELECTOR> (<EVENT_NAME>)="<CODE>"> </<COMPONENT_SELECTOR>>
Structural Directives[edit]
Structural directives are directives which change the DOM layout by adding and removing DOM elements. They are generally are prefixed by an asterisk, *.
Build-In Directives[edit]
- [ngClass] // to set a style via a class
- [ngStyle] // to set inline styles
- [(ngModel)] // to bind properties
- [ngIf]
*ngIf='<PROPERTY_NAME>' // shows tag only if property is true
- [ngFor]
*ngFor="let todo of todos"
- [ngSwitch]
- <ng-container>
Communication and Passing Data between Components[edit]
Parent to Child Communication[edit]
- create an input class property in the child component or use the input array of the @Component decorator e.g.
@Input() myProperty: number
@Component({
selector: 'child-component',
inputs: ['count'],
...
- and in the parent component template e.g.
<child-component [myProperty]=value></child-component>
- if needed react on changes (see here)
=====Child to Parent Communication=====,
- see here (e.g. by Events, Output decorator, ViewChild(), ...)
Services[edit]
Services provide specific functionality not directly related to views. Service providers can be injected into components as dependencies, making your code modular, reusable, and efficient. Modules, components and services are classes that use decorators. These decorators mark their type and provide metadata that tells Angular how to use them.
Services only live inside the scope of their providers, so in the scope of a module or a single component. They are instantiated when injected for the first time and keept alive as long as the provider exists. As services are normal classes, angulars lifecycle hooks do not apply to them.
Angular Decorators[edit]
ViewChild[edit]
ViewChild is a property decorator that configures a view query. View queries are set before the ngAfterViewInit callback is called.
Observables[edit]
The observable (see RxJS) pattern heavily used in Angular (see also Angular documentation).
// create an observable
timer$ = new Observable<string>( // new observable
observer => { // subscriber function is executed when a consumer calls subscribe() and desribes how to generate values
setInterval(
() => observer.next(new Date().toString()),
10000);
console.log("someone subscribed");
}
);
var subscription: Subscription = timer$.subscribe({ // passing an observer which is an objects that defines the handler for the values it receives
next(datestring) { // implements the Observer interface with callback methods for the 3 types of notifications
console.log(datestring); // next (required), error and complete (optional)
},
complete() {
console.log("timer1_1 completed");
}
});
Dependency Injection[edit]
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
constructur(private <PROPERTY_NAME>: <TYP>) // depency injection
Routing[edit]
In Angular, the best practice is to load and configure the router in a separate, top-level module that is dedicated to routing and imported by the root AppModule. By convention, the module class name is AppRoutingModule and it belongs in the app-routing.module.ts in the src/app folder, which contains a routing table (sequence is important!!!):
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: , component: LoginComponent}, // app root
{ path: 'bookmarks/menus/:id', component: MenuComponent},
{ path: 'welcome/:name', component: WelcomeComponent}, // parameter
{ path: '**', component: ErrorComponent} // matches everything
];
and in template:
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
and in code:
// see bookmarks.component.ts
this.router.navigate(
['/menus', this.currentSubMenuObjects[subMenuIndex].uuid], // setting required route parameter
{ queryParams: { mode: "view"} } // setting query parameter
);
Route Information[edit]
To get information of the route in the target component include in the ctor:
private route: ActivatedRoute,
and
// by snapshot
this.uuid = this.route.snapshot.paramMap.get('uuid');
this.mode = this.route.snapshot.queryParamMap.get('mode');
// by observer
this.id = +this.route.snapshot.params['id']; // to get parts of the
this.route.queryParams.subscribe(params => {this.parentId = +params['parentId'];}); // to get query params
PWA[edit]
Progressive Web Apps (PWA) rely on Service Workers. Service workers essentially act as proxy servers that sit between web applications, the browser, and the network (when available). They are intended, among other things, to enable the creation of effective offline experiences, intercept network requests and take appropriate action based on whether the network is available, and update assets residing on the server. They will also allow access to push notifications and background sync APIs.
When an application is loaded it is provided from the cache. In the background the service worker checks for an update and loads it to the cache. The new one is used next time the application is loaded. The version information is generated during build in ngsw.json.
Implementation[edit]
- Angular University detailed step by step guide or
- The complete Guide to Service Workers
- Progressive Web App (PWA)
ng add @angular/pwa
- creates e.g.
ngsw-config.jsonwhich format is described here
Debug Information[edit]
- description
- see http://<URL>:<PORT>/ngsw/state e.g. http://127.0.0.1:8082/ngsw/state output
[=== Version <HASH> Clients ... // clients with this version, could also be different tabs]
Version Management[edit]
Here is a solution if the version update should be done immediately when the application is loaded.
Angular Framework Modules[edit]
- BrowserModule
- Core
- @Component
- Template Driven Forms (FormsModule)
- HTTPModule
- Reactive Forms (ReactiveFormsModule)
- NgModule
Template Driven Forms[edit]
import {FormsModule} from "@angular/forms";
Reactive Forms[edit]
- see official documentation
- example see
menu.component.tsandmenu.component.htmlorconfiguration.component
import {ReactiveFormsModule} from "@angular/forms";
[formGroup]directiveFormBuilder.group()setValue() or patchValue()- subscribe if needed
HTTPModule[edit]
- usage
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable, throwError } from 'rxjs';
import { catchError, retry } from 'rxjs/operators';
- there are multiple overloads of
get() - observables in general can emit multiple values but an observable returned by the get() method only emits once
- All observables returned from HttpClient methods are cold by design. Calling
subscribe()triggers execution of the observable and causes HttpClient to compose and send the HTTP request to the server. - Completion or Error are mutually exclusive.
- resources
Angular CLI[edit]
Angular Command Line Interface
ng ng help ng version
Add[edit]
ng add
Build[edit]
ng build [--configuration production] // if production configuration build takes environment.prod.ts configuration, else environment.ts; --prod deprecated
creates dist folder, which can be copied directly to a web server. The difference between prod and dev build is described here.
E2E[edit]
ng e2e
runs and test the entire application, uses protractor. All tests are defined in folder e2e.
Generate[edit]
Component[edit]
<APP_ROOT_DIR>> ng g[enerate] c[omponent] <COMPONENT_NAME> // leaf the Component part of the name, it will be added automatically, e.g. ng g c app-header // e.g. <ROOT_DIR>>ng g c features/bookmarks
generates
/src/app/<COMPONENT_NAME>/*
and modifies app.module.ts. If COMPONENT_NAME starts with a small letter, the generated Typescript class and the NgModule declaration starts with a capital letter.
<APP_ROOT_DIR>/src/app/<COMPONENT_DIR>>ng g c <COMPONENT_NAME> // generates new component in /src/app/<COMPONENT_DIR>/<COMPONENT_NAME>/* <APP_ROOT_DIR>/src/app>ng g c <COMPONENT_NAME> // generates new component in /src/app/<COMPONENT_NAME>/*
Module[edit]
ng g m <MODULE_NAME> // generates /src/app/<MODULE_NAME>/<MODULE_NAME>.modules.ts
Service[edit]
ng generate service <PATH>/<SERVICE_NAME>
generates
/src/app/<PATH>/<SERVICE_NAME>.service.ts
Lint[edit]
ng lint
all rules are in tslint.json.
New[edit]
ng new <APP_NAME>
creates:
\<APP_NAME>\src\index.html // which contains the <app-root> tag \<APP_NAME>\src\app.component.ts // defines the root component class including <app-root> tag \<APP_NAME>\src\app.component.html // defines the root component template \<APP_NAME>\src\app-routing.modules.ts // contains all routings \<APP_NAME>\src\styles.css \<APP_NAME>\src\main.ts // bootstraps the root module which itself bootstraps the root component due to the bootstrap element of the @NgModule decorator platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule) \<APP_NAME>\src\app\app.module.ts // defines the root module
Test[edit]
ng test
uses Jasmine and Karma? and performs unit tests, see app.component.spec.ts
Serve[edit]
ng serve [--open // opens a browser with http://localhost:4200] [--port <PORT>]
polls for code changes, builds it and loads it in the browser.
Files and Directories[edit]
/angular.json
This file contains the settings of the Angular project (see here).
/tsconfig.json
describes the translation from Typescript to Javascript.
/README.md
contains documentation.
/package.json
contains all dependencies, frameworks and tools.
/src/polyfill.ts
manages all browser incompabilities for Javascript.
/src/styles.css
contains all css styles for apps.
/src/app/
contains all modules and components.
/src/assets/
contains images
/src/environments/
contains configurations for all environments like test, integration, qa, ...
/src/node_modules
all packages and frameworks installed due to listing in package.json.
Style Guide[edit]
Installation[edit]
npm install -g @angular/cli // -g installs Angular CLI it globally, not project-specific ng // Angular cli ng version // prints version
cd C:\Uwes\typescripts\ mkdir angular // for examples and tests
Update[edit]
ng update // gives a list which can be updated manually by ng update @angular/<COMPONENT>, but everything has to be committed before
Frontend Frameworks[edit]
- Angular Material seems to be the best choice
- jqWidgets
Examples[edit]
Test1[edit]
cd C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular ng new test1 // enforces strict type checking yes, router yes, CSS, cd test1 ng serve http://localhost:4200/ CTRL + C ... ng create services/data/messageData
uweheuer Frontend (obsolete)[edit]
- new version see New UweHeuer Frontend
cd C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular ng new uh-fe // strict type checking, router, CSS cd uh-fe ng add @angular/material // adds Angular Material, Indigo, no typography, browser animation // test by editing app.component.html ng g m material // generates module // add import to app.module.ts ng g c features/bookmarks ng g c features/authentication ng g c features/home ng g c features/externals ng g c layout/header ng g c layout/footer ng g c layout/sidenav C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular\uh-fe\src\app\features\bookmarks> ng g c menu C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular\uh-fe> ng generate service services/backend/menuData C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular\uh-fe> ng generate service services/backend/bookmarksData C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular\uh-fe> ng generate service services/uiState C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular\uh-fe> npm i angular2-uuid -s
Test Layout1[edit]
cd cd C:\Uwes\typescripts\angular ng new layout-test1 // strict type checking, router, CSS cd layout-test1 npm i -s @angular/flex-layout @angular/cdk // from https://github.com/angular/flex-layout // add FlexLayoutModule to app.modules.ts
ToDos[edit]
- API Testtools e.g. Postman
- single menu REST API
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44007188/deserialize-json-with-spring-unresolved-forward-references-jackson-exception
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17393812/json-and-java-circular-reference
- https://www.baeldung.com/jackson-bidirectional-relationships-and-infinite-recursion
- https://github.com/jsog/jsog-jackson
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-data-rest-relationships
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23767233/spring-data-rest-post-new-entity-with-relationships
- https://reflectoring.io/relations-with-spring-data-rest/
- https://softwarehut.com/blog/tech/spring-data-rest-quick-easy-rest-jpa
- UUID
- Menu and Url associative array
- Component State
- https://offering.solutions/blog/articles/2018/11/21/online-and-offline-sync-with-angular-and-indexeddb/
- Progressive Web App (PWA) (IndexedDB)
- Toolboar for total app navigation
- Toogle Group with Icons for Bookmarks View
- Sidenav for full app
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/angular-material-toggle-sidenav-in-another-component?file=src%2Fapp%2Flayouts%2Fdrawer%2Fdrawer.component.ts
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48073057/open-close-sidenav-from-another-component
- https://stackblitz.com/angular/lyabryrmmpk?file=src%2Fapp%2Fsidenav-backdrop-example.html
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/56357598/how-to-toggle-mat-sidenav-in-another-component?rq=1
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40820354/setting-sidenav-below-toolbar-in-angular-material-design?rq=1
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/angular-v6xwte?file=src%2Fapp%2Fapp.component.html
- Angular Forms Module
- Flex Layout
- adding components dynamically
- add Host Listener
- Menu
- http://embed.plnkr.co/0I8C8RbhvyoEjEoLZksz/ Menu Trigger Data
- Bookmark Tree View
- https://medium.com/@vag/angular-material-tree-26adccadc63b
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/angular-ax72ew?file=app%2Ftree-checklist-example.ts
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/angular-material-nested-tree-with-updates?file=src%2Fapp%2Ftree-datasource.ts
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s0Vy3sLbeyA
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/material-tree-flat
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/material-tree-nested nested tree with lines
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/material-tree-checklist
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/material-tree flat tree with icon (best fit)
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/material-tree-dynamic with loading animmation
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/angular-material-tree-example
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BALaj39rbZE flat tree with check boxes
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/ng-mat-tree-test-7 nested tree with icons
- https://blog.briebug.com/blog/angular-how-to-implement-drag-and-drop-in-a-material-tree Drag and Drop
Resources[edit]
- Official Getting Started
- Official Documentation
- C:\Uwes\owncloud\documents\Software_Development\Programming\Frameworks\Angular\Angular.drawio
- Angular University Beginners Course
- Angular Wiki