Magento
ToDo[edit]
- select options for custom attribute not by plugin but as parameter of addAttribute() https://magento.stackexchange.com/questions/160796/magento-2-custom-customer-attributes-with-select-list
- addAttribute() parameter in my Wiki https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.3/extension-dev-guide/attributes.html
General[edit]
- Magento 2 was released in July 2015
- Variants
- Magento Open Source (before 2018 Magento Community Edition)
- Magento Commerce (before Magento Enterprise Edition)
- Differences see here
- object oriented
- uses design patterns (GoF) like GRASP, but in an individual manner
- uses MVC with thin controller approach (Business Logic is mainly in Model or View), View is configured by layout XML
- user groups:
- web business user
- system administrator
- web API user
Concepts[edit]
In the backend the configuration of the three concepts below are 'Stores' menu.
- Websites corresponds to a Webshop
- common database
- common installation
- different products
- different customer
- different checkouts
- different shopping cart
- Stores
- different products
- common customer
- common checkout
- common shopping cart
- Store View
- common products
- common customer
- common checkout
- common shopping cart
- different user interface (layout, language, ...)
Technology[edit]
- PHP 7 according to standards
- MySQL 5.6
- Apache 2.2, 2.4
- PHP Composer
- HTML5
- LESS CSS
- jQuery
- RequireJS
- Zend Framework
- [[1]]
- Magento Testing Framework
- ...
Coding Standards[edit]
PHP[edit]
- follows PSR 1 to 4
Patterns[edit]
Factory[edit]
Factories are strongly linked to Repositories. Repositories are part of the Service Contracts (they are implementations of interfaces in Api), this means they are meant as public interface to other modules. Repositories do not come with methods to create a new entity, so in that case you will need a factory. But use the factory for the interface, such as Magento\Catalog\Api\Data\ProductInterfaceFactory - it will create the right implementation based on DI configuration.
- create()
$c = $this->objectManager->get('\Magento\Customer\Api\Data\CustomerInterfaceFactory')->create(); // or
$c = $this->customerInterfaceFactory->create(); // or
$c = $this->objectManager->create(\Magento\Customer\Api\Data\CustomerInterface::class);
- load()
$object = $this->customerRepositoryInterface->get("name"); // this is best but also possible
$object = $this->myFactory->create(); $object->load($myId);
- save()
$c = $this->customerRepositoryInterface->save($c); // this is best, but also possible
$object->setData('something', 'somethingDifferent')->save();
Repository[edit]
A repository object is responsible for reading and writing your object information to an object store (i.e. a database, the file system, physical memory, etc.). Naming convention is <Entity>RepositoryInterface. Methods are:
- save(../Api/Data/<Entity>Interface $object2Save)
- get()
- getById()
- getList()
- delete()
- deleteById()
- load
$repo = $this->myRepository(); $object = $repo->getById($myId);
- save
$object->setData('something', 'somethingDifferent');
$repo->save($object);
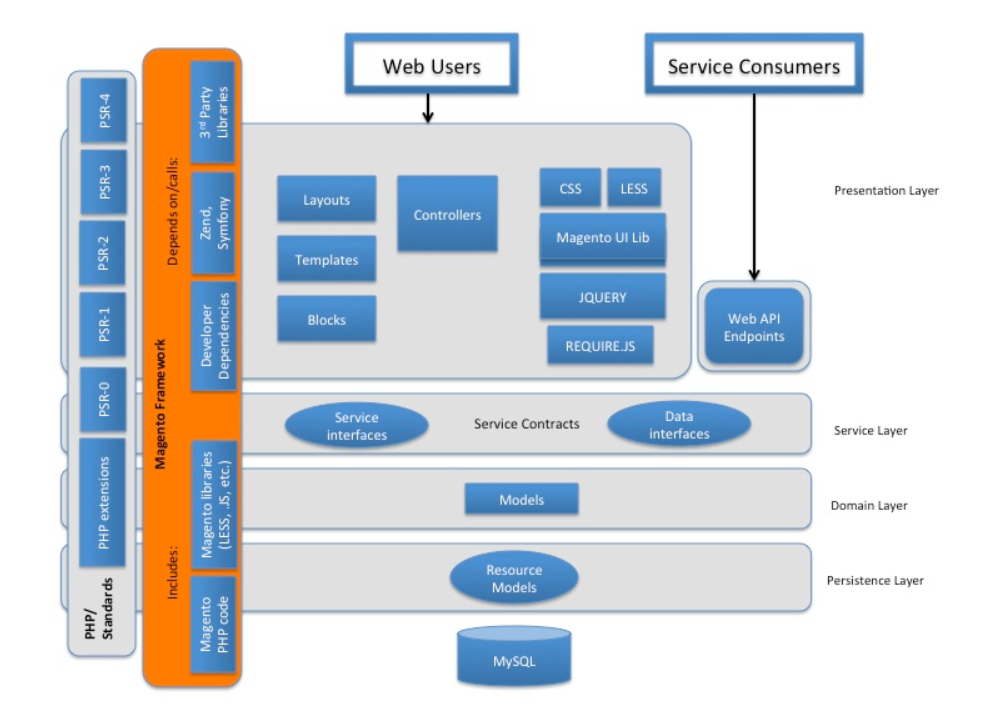
Basic Software Architecture[edit]
Magento Software Architecture[edit]
- layers:
- presentation
- service
- domain
- persistence
Presentation Layer[edit]
The graphic and appearance information is called (custom) theme. A theme is a component of Magento application which provides a consistent look and feel (visual design) for entire application area (for example, storefront or Magento admin) using a combination of custom templates, layouts, styles or images. Out-of-the-box Magento application provides two design themes: Luma, as a demonstration theme, and Blank as a basis for custom theme creation. Theme Layout files provided by themes:
- Page configuration and generic layout files:
<THEME_DIR>/<Namespace>_<Module>/layout
Page layout files:
<THEME_DIR>/<Namespace>_<Module>/page_layout
The default or standard layouts are located in:
<MAGENTO_DIR>/vendor/magento/module-theme/view/frontend/layout/default.xml <MOGENTO_DIR>/vendor/magento/module-backend/view/adminhtml/layout/default.xml <MOGENTO_DIR>/vendor/magento/theme-frontend-luma/ // Luma theme
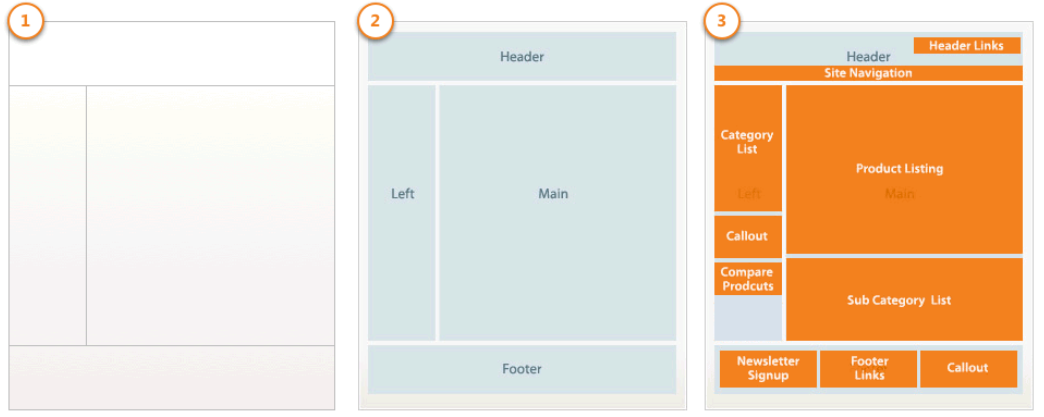
The basic components of page design are
- layouts: structure of a web page using an XML file that identifies all the containers and blocks composing the page (1)
- containers: placeholders within that web page structure assigning content structure to a page using container tags within a layout XML file (2)
- blocks: render the UI components on a page using block tags within a layout XML file (3)
- templates: blocks use templates to generate the HTML to insert into its parent structural block
There are two options to influence the layout: override or extend. Extending layout file is used for modifying of the default one, without replacing, but сhanging and amplifying it with the instructions. If you need to make a lot of changes or if the layout file contains an instruction that we can not change in the file extension, then the only option will be to override such file. The difference and how-to is described here.
UI Components[edit]
Magento UI components are implemented as a standard module named Magento_UI (see official doc).
Service Layer[edit]
- bridges presentation and domain layer
- provides service contracts (PHP interface, REST/SOAP API): a service contract is a set of PHP interfaces that is defined by a module. This contract comprises data interfaces and service interfaces. It is recommended to use Magento’s existing service contracts e.g.
Magento\Sales\Api\Data\OrderInterface(in <MAGENTO_DIR>\vendor\magento\module-sales\Api\Data\OrderInterface.php) rather thanMagento\Sales\Model\Order.
Business/Domain Layer[edit]
- implementents the business logic
- modul communication via event events and observers, plugins and di.xml
Persistance Layer[edit]
- see official documentation
- implements CRUD (create, read, update, delete) requests
- there are 3 types of classes:
- model classes: don't contain any code for communicating with the DB (base class
\Magento\Framework\Model\AbstractModel) - resource classes: read and write to the DB
- collection classes: array of individual model instances which implement IteratorAggregate and Countable
- model classes: don't contain any code for communicating with the DB (base class
- models and resources are often seen as an unified thing called model
Adding Attributes to Entities[edit]
- there are two ways to extend attributes: custom attributes and extension attributes.
Extension Attributes[edit]
Every interface that extends \Magento\Framework\Api\ExtensibleDataInterface can be extended by extension attributes.
- /etc/extension_attributes.xml
- interface declaration
Events and Observers[edit]
Events are dispatched by Magento 2 modules whenever specific actions are triggered. When an event dispatches, it passes data to the observer that is configured to watch (or monitor) that event. You can dispatch Magento 2 Events using the Magento\Framework\Event\Manager class. This class can be obtained through dependency injection by defining the dependency in the constructor method of the class. Observers are executed whenever a specific event for which they were set to listen is triggered.
For implemention see here.
payment_method_is_active[edit]
- called in \vendor\magento\module-payment\Model\Method\AbstractMethod->isAvailable() (search for event => around line 864)
- parameter:
- result as DataObject
- methodInstance as AbstractMethod
- quote as CartInterface (see \vendor\magento\module-quote\Api\Data\CartInterface.php)
Collections[edit]
Documentation is good in Kindle book.
$customerCollection = $this->customerFactory->create();
$customerCollection->addAttributeToFilter('created_at', ['to' => $dl]);
Modules[edit]
A Magento module is a directory with subdirectories containing blocks, controllers, helpers, and models that are needed to create a specific store feature. It has a life cycle that allows them to be installed, deleted, or disabled. Modules typically live in the vendor directory of a Magento installation, in a directory with the following PSR-0 compliant format: vendor/<VENDORNAME>/<MODULENAME> or you can just create the app/code/<VENDORNAME>/<MODULENAME> directory (<MODULE_ROOT_DIR>) and the required directories within it. Inside the <MODULE_ROOT_DIR> you will find all the code related to this module. The name used for registration is usually <VENDORNAME>_<MODULENAME>.
registration.php[edit]
- mandatory
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>|<THEME_ROOT_DIR>/registration.php
<?php \Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::register( \Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::MODULE, // or \Magento\Framework\Component\ComponentRegistrar::THEME 'Wendweb_BrinkmannCustomer', // see DB table setup_module __DIR__ );
module.xml[edit]
- mandatory
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/etc/module.xml declares the module by configuration like name, version, dependencies, ...
<config>
<module name="<VENDORNAME>_<MODULENAME>" setup_version="<MAJOR_VERSION>.<MINOR_VERSION>.<PATCH_VERSION>">
[<sequence>
<module name ="<VENDORNAME>_<MODULENAME>" />
<DEPENDENCY_LIST>
</sequence>]
</module>
</config>
config.xml[edit]
- optional
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/etc/config.xml
- system configuration file (official documentation)
- the default values of the attributes are somehow the 'reset to factory values', they are used if no corresponding XPath DB entry is found in table core_config_data
- if a module is deinstalled or the name or path is changed they have to be deleted manually from the DB
General[edit]
<config>
<default>
[<section_id>|<CARRIERS_SECTION> // see system.xml
<group_id> // see system.xml
<field_id>...</field_id> // see system.xml
...
</group_id>
</section_id>]
<CARRIERS>
</default>
</config>
Carriers[edit]
- A Carrier represents a shipping carrier, just like in real world (ex. FedEx).
- XPath (e.g. in table core_config_data) is carriers/<CODENAME>/<ATTRIBUTE>
...
<default>
<carriers> // carries is for shipping, other options ???
<<CODENAME>> // same as $_code property in model class
<<CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE>><SYSTEM_DEFAULT_VALUE></<CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE>> // name used in system.xml and in code
<active><0|???></active> // mandatory, active or not
<model>
<FILEPATH_FILENAME_WO_EXT> // mandatory, model class with same name as FILENAME
</model>
<title><TEXT></title> // mandatory, displayed in the frontend as name of shipping carrier and in backend as title
<sallowspecific><0|1></sallowspecific> // mandatory, for carries: available in all countries or only in selected countries
<sort_order></sort_order> // mandatory
<name><TEXT></name> // optional, shown in frontend as name of shipping method and in backend as method
</<CODENAME>>
</carriers>
</default>
webapi.xml[edit]
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/etc/webapi.xml
- Magento relies on PHP doc in the methods of the named service class, especially @param and @return annotations
system.xml[edit]
- optional
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/etc/adminhtml/system.xml
- default values in config.xml
- used for Magento system configuration
...
<system>
...
<section id=["carriers"|"<NAME>"]>
...
<group id="<CODENAME>"> // same as $_code attribute in shipping class and config.xml
<label><LABEL></label>
<field id="<CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE>" type="<TYPE>"> // for TYPEs see /magento/framework/Data/Form/Element/Renderer/Factory.php row 26 or here
<label><LABEL></label>
[<validate><VALIDATE>{ <VALIDATE>}</validate>] // see below for standard or here for custom validation
[<source_model><MODEL></source_model>]
[<frontend_class><CLASS></frontend_class>]
[<comment><COMMENT></comment>] // will be displayed in small letters below the field
[<tooltip><TOOL_TIP></tooltip>]
[<backend_model><CLASS_NAMESPACE></backend_model>] // e.g. used for server side validation
</field>
...
</group>
</section>
</system>
VALIDATE := // see here
'validate-no-html-tags' => 'HTML tags are not allowed'
'validate-select' => 'Please select an option.'
'validate-no-empty'
'validate-alphanum-with-spaces'
'validate-street'
'validate-phoneStrict'
'validate-phoneLax'
'validate-fax'
'required-entry' => 'This is a required field.'
'validate-number' => 'Please enter a valid number in this field.'
'validate-digits' => 'Please use numbers only in this field. Please avoid spaces or other characters such as dots or commas.'
'validate-date' => 'Please enter a valid date.'
'validate-email' => 'Please enter a valid email address. For example johndoe@domain.com.'
'validate-emailSender'
'validate-password'
'validate-admin-password'
'validate-url' => 'Please enter a valid URL. Protocol is required (http://, https:// or ftp://)'
'validate-clean-url'
'validate-xml-identifier'
'validate-ssn'
'validate-zip-us'
'validate-date-au'
'validate-currency-dollar'
'validate-not-negative-number' => 'Please enter a number 0 or greater in this field.'
'validate-zero-or-greater' => 'Please enter a number 0 or greater in this field.'
'validate-state' => 'Please select State/Province.'
'validate-cc-number' => 'Please enter a valid credit card number.'
'validate-data' => 'Please use only letters (a-z or A-Z), numbers (0-9) or underscore(_) in this field, first character should be a letter.'
- all elements below <system> have the following attributes:
- showInDefault=["0"|"1"], showInWebsite=["0"|"1"] and showInStore=["0"|"1"] which control whether the element is shown in the corresponding configuration level.
- data is stored in stored in DB table 'core_config_data' with key <SECTION_ID>/<GROUP_ID>/<FIELD_ID>
Custom Client Validation[edit]
acl.xml[edit]
- optional
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/etc/acl.xml
Controller[edit]
For an example see here
Controller is a class located in module Controller folder, responsible for specific Url or group of Url’s. All controllers extend \Magento\Framework\App\Action\Action. There are two different Controller, for frontend and for backend.
routes.xml[edit]
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/etc/(frontend|adminhtml)/routes.xml
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:App/etc/routes.xsd"> <router id="(standard|admin)"> <route id="<ROUTE_NAME>" frontName="<FRONT_NAME>"> <module name="<MODULE_NAME>" /> </route> </router> </config>
- defines controller
- called by <SHOP_URL>/<FRONT_NAME>/<ACTION_PATH>/<ACTION_CLASSNAME>, where ACTION_PATH is the sub-directory tree below the controller directory
<MODULE_ROOT_DIR>\Controller\.
Model Classes[edit]
- module declaration in <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Model/
Simple Model[edit]
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Model/[<SUB_DIR>/]<MODELNAME>.php
class <MODELNAME> extends \Magento\Framework\Model\AbstractModel
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_init('<VENDORNAME>\<MODULENAME>\Model\ResourceModel\<MODELNAME>'); // tells Magento about resource class
- resource declaration in <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Model/ResourceModel/<MODELNAME>.php
class <MODELNAME> extends \Magento\Framework\Model\ResourceModel\Db\AbstractDb
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_init('<TABLENAME>', '<PRIMARY_KEY_COLUMN>');
- create collection in <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Model/ResourceModel/<MODELNAME>/Collection.php
class Collection extends \Magento\Framework\Model\ResourceModel\Db\Collection\AbstractCollection
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_init('<FULL_MODEL_CLASSNAME>', '<FULL_RESOURCE_CLASSNAME>');
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Model/<MODELNAME>.php
class <MODELNAME> extends \Magento\Framework\Model\AbstractModel
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_init('<VENDORNAME>\<MODULENAME>\Model\ResourceModel\<MODELNAME>'); // tells Magento about resource class
- resource declaration in <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Model/ResourceModel/<MODELNAME>.php
class <MODELNAME> extends \Magento\Framework\Model\Entity\AbstractEntity
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_read =
$this->_write =
}
public function getEntityType()
{
...
}
- create collection in <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Model/ResourceModel/<MODELNAME>/Collection.php
class Collection extends \Magento\Framework\Model\ResourceModel\Db\Collection\AbstractCollection
{
protected function _construct()
{
$this->_init('<FULL_MODEL_CLASSNAME>', '<FULL_RESOURCE_CLASSNAME>');
Observer[edit]
- definition
/etc/events.xml // global events /adminhtml/events.xml /frontend/events.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Event/etc/events.xsd"> <event name="<EVENTNAME>"> <observer name="<MY_OBSERVER_NAME>" instance="<VENDORNAME>\<MODULENAME>\Observer\<CLASSNAME>" /> </event> </config>
- class file located in <MODULE_ROOT_DIR/Observer
class <MyObserverClass> implements ObserverInterface
{
public function execute(Observer $observer)
{
$parameter = $observer->getEvent->get<PARAMETER>(); // passed via eventManager->dispatch(<EVENTNAME>,
// [ <PARAMETER> => $parameter ]);
- to find out which parameter are passed via standard events search M2 source code for event and look up parameter
Setup/Uninstall[edit]
- see here when which method is called
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Setup
InstallData.php InstallSchema.php Recurring.php // run every time magento setup:upgrade is run Uninstall.php UpgradeData.php UpgradeSchema.php
Base Layout[edit]
Base Layout files are provided by modules. Conventional location
- Page configuration and generic layout files:
<MODULE_DIR>/view/frontend/layout
- Page layout files:
<MODULE_DIR>/view/frontend/page_layout
UI[edit]
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Ui
Views[edit]
- /view/adminhtml
- /view/frontend
Api[edit]
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Api contains the repository interface.
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Api/Data contains the data interface of the model (e.g. getter and setter) and the search result interface.
Helper[edit]
- /Helper
Console[edit]
- /Console
Localization[edit]
- /i18n
Block[edit]
- <MODULE_ROOT_DIR>/Block
Plugins[edit]
A plugin, or interceptor, is a class that modifies the behavior of public class functions by intercepting a function call and running code before, after, or around that function call. Plugins allow you to target changing/adding/removing functionality on the method level. Magento 2 plugins allow us to execute code before (e.g. to change parameter of the standard method), after (e.g. to change the output of the standard method) or around any public method.
The di.xml file in your module declares a plugin for a class object.
<config>
<type name="{ObservedType}">
<plugin name="{pluginName}" type="{PluginClassName}" sortOrder="1" disabled="false" />
</type>
</config>
Conention is to name the PluginClassName as \<VENDOR>\<MODULE>\Plugin\<MODEL>Plugin.
Before Methods[edit]
Magento runs all before methods ahead of the call to an observed method. These methods must have the same name as the observed method with ‘before’ as the prefix and first parameter must of type of the model. It is usually used to modifiy the arguments.
After Methods[edit]
Magento runs all after methods following the completion of the observed method. Magento requires these methods have a return value and they must have the same name as the observed method with ‘after’ as the prefix.
public function after<MethodName>(
<ClassOfOriginalMethod> $subject,
$result, // result of the orginal method
<ParameterListOfOrginalMethod>) // all which are used from left to right, the most rightest is the last parameter needed
{
// to modify the original result, change $result and return it
}
Around Methods[edit]
Magento runs the code in around methods before and after their observed methods. Using these methods allow you to override an observed method. Around methods must have the same name as the observed method with ‘around’ as the prefix.
- /Plugin
Commands[edit]
- see here or UweHeuer testcmd
Caching[edit]
- located in /var/ directory
Code Generation[edit]
- Factory, Proxy and Interceptor classes are generated and stored in /var/generation/
Custom Attributes[edit]
Different factories have to be used for different entities:
- CustomerSetupFactory
- Customer
- Customer Address
- SalesSetupFactory
- CreditMemo
- Invoice
- Order
- QuoteSetupFactory
- Quote
- QuoteItem
- QuotePayment
- CategorySetupFactory
- Category
- Product
DB Model[edit]
Obviously Magento uses a flat model and a flexible attribute model called EAV. To lookup which model is used for what there are different sources. One is setup classes e.g. SalesSetup which contains a protected variable '$_flatEntityTables'.
Flat Model[edit]
EAV Model[edit]
- Entity Attribute Value (EAV)
- the list of (system???) entities can be found in the DB table 'eav_entity_type' incl. the tpye ID and the name of the table with the entity instances e.g.
- entity_type_id='1'
- entity_type_code='customer'
- entity_table='customer_entity'
- additional_attribute_table='customer_eav_attribute'
- the list of all EAV attributes of all entities are in DB table 'eav_attribute' incl. the backend type. The values of the attributes are in table '<ENTITY_TYPE_CODE>_entity_<BACKEND_TYPE>'. If the backend type is 'static' than the values are in corresponding columns in the entity table.
- for some entities like customer there is a table '<ENTITY_TYPE_CODE>_eav_attribute' with additional information like validation rules. Entries are obviously not deleted if a attribute is deleted programmatically.
DB Tables[edit]
- core_config_data: e.g. data from config.xml, system.xml
- eav_entity_type: e.g. Customer, CatalogProduct, Order, ...
- setup_module: all modules and their versions
Areas[edit]
Catalog and Products[edit]
- Admin -> Catalog -> Products
Custom Attributes[edit]
- Stores -> Attributes Section -> Product -> Add New Attribute
- Catalog -> Products -> Edit -> Add Attribute -> Select -> Add Selected
- assignment in Attributes section
Guest Orders[edit]
- System menu -> Configuration -> Checkout button in the Sales section on the left -> Checkout Options panel on the right. After you expand the Checkout Options panel you'll see a drop-down menu Allow Guest Checkout
Customer[edit]
- Magento 2.x applies the new SHA-256 hashing algorithm over the old MD5 in Magento 1. SHA-256 stands for Secure Hash Algorithm which is used in Magento 2 to hash passwords.
- The Magento_Customer module uses the EAV structure to store customer data. Thus, there is no single table that stores customer information. Rather, multiple tables exist, depending on the customer property and its data type.
- /vendor/magento/module-customer/view/frontend/layout/customer_account_edit.xml
Logging[edit]
- logging goes to
<MAGENTO_DIR>\var\logor if an error record it is report in<MAGENTO_DIR>\var\log\report\<ID> - see good description in https://black.bird.eu/en/blog/magento2logs.html or http://www.thienphucvx.com/magento-2-logging-to-a-custom-file/
- log output is generated by constructor injection PSR-3 interface
\Psr\Log\LoggerInterface $loggerwhich is implemented inMAGENTO_DIR>\vendor\psr\log\Psr\Log - interface is implemented by Monolog library located in
<MAGENTO_DIR>\vendor\monolog\monolog, this mapping is defined in <MAGENTO_DIR>/app/etc/di.xml by<preference for="Psr\Log\LoggerInterface" type="Magento\Framework\Logger\Monolog"/>
Shipping[edit]
- Admin -> Stores -> Configuraton -> Sales -> Shipping Settings -> Origin
- Admin -> Stores -> Configuraton -> Sales -> Shipping Methods or Admin -> Shops -> Konfiguration -> Umsatz -> Versandmethoden
- internally the term method also refers to something like 'standard' or 'express
- official documentation to customize shipping in checkout
- programmatically:
$method->setMethodTitle(); $method->setMethod();$method->setCarrierTitle();$method->setCarrier();
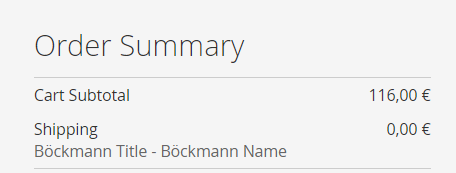
- table sales_order->shipping_description has <CARRIERTITLE>-<METHODTITLE>
- table sales_order->shipping_method has <CARRIER>_<METHOD>
- table sales_order_grid->shipping_information has <CARRIERTITLE>-<METHODTITLE>
- table quote_shipping_rate->carrier has <CARRIER>
- table quote_shipping_rate->carrier_title has <CARRIERTITLE>
- table quote_shipping_rate->code has <CARRIER>_<METHOD>
- table quote_shipping_rate->method has <METHOD>
- table quote_shipping_rate->method_title has <METHODTITLE>
Prices[edit]
- SubTotal: in customer currency
- BaseSubTotal: in shop's base currency
Currency[edit]
- Admin -> Stores -> Configuration -> General -> Currency Setup
Admin[edit]
- Left area (Dashboard down to System, ...) is called menu
- Timeout: Stores > Settings > Configuration > Advanced > Admin > Security > Admin Session Lifetime (seconds)
ACL[edit]
M2 can have unlimited roles, each having a list of ACL rules.
- System -> Benutzerrollen -> Click on Role -> Rollen-Resourcen
Object Model[edit]
- Stock Keeping Unit (SKU), dedicated product id within a shop
AbstractCarrier[edit]
- \Magento\Shipping\Model\Carrier\
- Base class for shipping with major methods for shipping models.
AbstractDb[edit]
- \Magento\Framework\Model\ResourceModel\Db\
- resource model base class
AbstractEntity[edit]
- \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\
- EAV resource model base class
AbstractModel[edit]
- AbstractModel
- \Magento\Framework\Model\
- EAV model base class
Attribute[edit]
- table 'eav_attribute'
- ???system attributes are by default part of every attribute set
Attribute Group[edit]
- combination of attributes e.g. to group them on a tab in backend
- table 'eav_attribute_group'
Attribute Set[edit]
- set of attribute groups (see in official documentation)
- the default attribute set is something like the factory proposal, but you can even add attributes to the default w/o creating a new set
- table 'eav_attribute_set'
CustomerSetup[edit]
- \Magento\Customer\Setup
- extends EavSetup
DataObject[edit]
- Magento\Framework\
- model base class
- Extension don't have to implement getter- and setter-, unset- and has-methods, DataObject implements getXYZ() and setXYZ() by overriding the PHP __call magic method
EavSetup[edit]
- Magento\Eav\Setup\
addSetup()[edit]
- type: which eav table is used
- label: label in admin area
- input: input type
- required:
- sort_order: in admin area
- globe: scope
- wysiwyg_enabled:
- is_html_allowed_on_front
Exception[edit]
- \Magento\Framework\
LocalizedException[edit]
- Magento\Framework\Exception\
- The ctor expects as a first parameter a Magento\Framework\Phrase object which can be created by the __() function defined in \app\functions.php and which is used to JSONize the information.
Mysql[edit]
- Magento\Framework\DB\Adapter\Pdo\Mysql
- extends \Zend_Db_Adapter_Pdo_Mysql implements AdapterInterface
RateRequest[edit]
- Magento\Quote\Model\Quote\Address\
- This class contains all information about items in cart/quote, weight, shipping address and so on.
SalesSetup[edit]
- Magento\Sales\Setup
- extends EavSetup
Directory and File Structure[edit]
- /app/code: for local developed modules
- /app/design/frontend/: for storefront themes
- /app/design/frontend/Magento/<theme>: for Magento themes
- /app/design/adminhtml: for admin themes
- /app/etc/
env.phpDB configuration
- /app/i18n: for language packages
- /pub/ web server should point to this directory
- /pub/static.php // entry point
- /vendor/magento/theme-frontend-<theme>: <theme> directory
- /var/generation: contains only? generated files
- /var/?: cached infos
Operations[edit]
Commands[edit]
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento cache:flush <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento cache:clean
Module Installation[edit]
copy to <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\app\code\ <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento module:status // first time for a new module module is listed as disabled <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento module:enable <MODULE_NAME> // adds module to /app/etc/config.php <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento setup:upgrade // see below
Upgrade Module[edit]
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento setup:upgrade // triggers setup scripts (if the module has one) of all modules that needs setup,
// and updates version info in table setup_module
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento setup:db-schema:upgrade
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento setup:db-data:upgrade
In Magento 2 upgrade is defined by the following rule (see here):
IF (NO 'schema_version' IN table 'setup_module') THEN InstallSchema ELSE UpgradeSchema ENDIF Recurring // Recurring Schema IF (NO 'data_version' IN table 'module_setup) THEN InstallData ELSEIF (version outdated) THEN UpgradeData ENDIF RecurringData
In order to manually upgrade a module:
delete row from DB table setup_module php magento setup:upgrade
Uninstall Module[edit]
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento magento module:uninstall // only works for modules defined by a composer package
Detailled steps to uninstall manually are described here
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento module:disable <MODULE_NAME> // sets module in /app/etc/config.php to 0 <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento setup:upgrade
DB Logging[edit]
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento dev:query-log:enable // writes all queries to /var/debug/db.log <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento dev:query-log:disable
Magento Mode[edit]
<MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento deploy:mode:show <MAGENTO_INSTALL_DIR>\bin\php magento deploy:mode:set developer
Indexing[edit]
php magento indexer:reindex // e.g. needed to show new customers in the admin customer list
Administration[edit]
php bin/magento admin:user:create [<PARAMETER>|--help] // will ask for all needed parameters
Configuration[edit]
Admin Session Timeout[edit]
- Stores->Settings->Configuration->Advanced->Admin->Security->Admin Session Lifetime
Admin URL[edit]
- lookup /app/etc/env.php
backend =>
Cache and Index Management[edit]
- System -> Tools -> Cache Management
Payments[edit]
- payments = zahlungsarten
- Stores->Configuration->Sales->Payment Methods
- banktransfer := Bank Transfer Payment (Überweisung, Vorkasse)
- cashondelivery := Cash on Delivery Payment (Nachnahme)
- checkmo := Check / Money Order (Kauf per Rechnung)
- purchaseorder := Purchase Order (Bestellung)
DB Dump[edit]
C:\Uwes\Programme\xampp7.0.31\mysql\bin>mysqldump.exe --user=root m2_1 >C:\temp\m2_1.txt
Error Logging[edit]
- decomment in \app\bootstrap.php
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
Debugging[edit]
- see here for some debugging strategies
Integration with PHPStorm[edit]
- mark the following directories as excluded for indexing:
\bin\ \dev\ \pub\ \setup\ \var\cache\ \var\log\ \var\page_cached\ \var\view_processed\
Magento Marketplace[edit]
- UweHeuerAccessKey
- Public Key: 6f7df3e4e393b84da74c41937990b227
- Private Key: a39505396b6112f47c43aa8c565cad8b
Installation[edit]
AWS[edit]
Hosting Guide for AWS
Computer[edit]
Version[edit]
To check the version:
- add
/magento_versionto the shop URL or - use MagentoVersion.com
- use magescan.com
- use magereport.com
- lookup footer of admin area
Sources[edit]
- Magento Marketplace
- free videos
- many Magento 2 articles
- Magento DevDocs
- PHP Developer Guide @ Magento DevDocs
- German Demo Shop
- Kindle Book 'Magento 2 Developer's Guide'
- German User Handbook